Understanding of CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing)
My Struggle
Every time I try to develop projects, especially when working on both frontend and backend, I encounter the same frustrating error:
“Access to fetch at ‘Your API URL’ from origin ‘Your Frontend URL’ has been blocked by CORS policy: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource.”
To fix this, I end up modifying the backend code. In my case, using a Flask Python backend, I add the flask_cors package to enable CORS for specific or all routes, and the error disappears.
But what’s happening under the hood? Why does this error occur? I spent some time researching and want to explain it in this article.
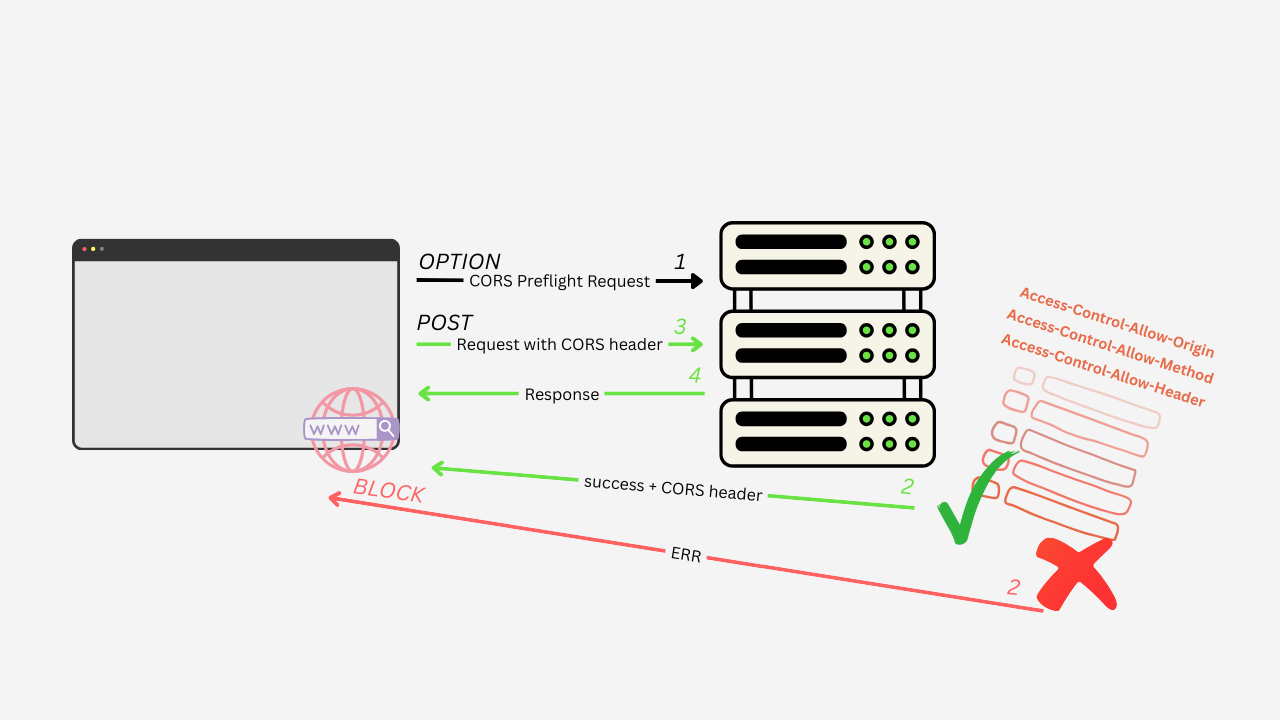
What is CORS?
CORS stands for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing. It’s a security mechanism that controls how resources are shared between different origins. A common example is a frontend application requesting data from a backend API.
To prevent unauthorized access to the backend, we configure which origins are allowed to access its resources. During development, I often use "*", which permits all origins to make requests, but this is not recommended for production.
How flask_cors Fixes the Issue
flask_cors handles the complexity of CORS preflight requests (HTTP OPTIONS requests) and ensures the backend communicates to the browser which origins, methods, and headers are allowed.
TBC…
Reference:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Security/Same-origin_policy
https://fetch.spec.whatwg.org/#http-cors-protocol
https://github.com/corydolphin/flask-cors